25. K 个一组翻转链表(Reverse Nodes in k-Group)H
英文题目
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
Follow up:
Could you solve the problem in O(1) extra memory space?
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example 1:
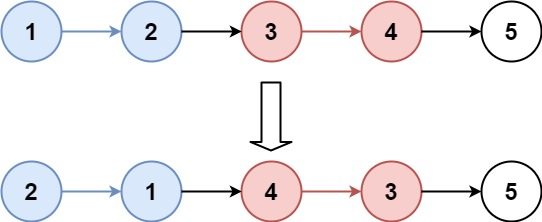
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [2,1,4,3,5]Example 2:
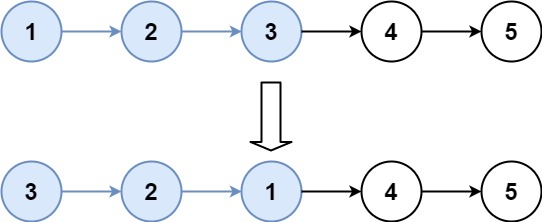
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 Output: [3,2,1,4,5]Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1 Output: [1,2,3,4,5]Example 4:
Input: head = [1], k = 1 Output: [1]Constraints:
The number of nodes in the list is in the range sz.
1 <= sz <= 5000
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 <= k <= sz
中文题目
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
进阶:
你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 输出:[3,2,1,4,5]示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]示例 4:
输入:head = [1], k = 1 输出:[1]提示:
列表中节点的数量在范围 sz 内
1 <= sz <= 5000
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 <= k <= sz
模拟法
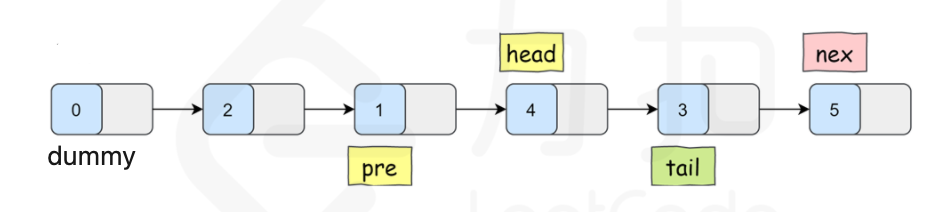
dummy为头指针的前一个指针,pre为待翻转链表前一个,head为待翻转链表的头指针,tail为待翻转链表的尾指针,nex为待翻转链表的尾指针的下一个指针
保持这个关系,然后每次翻转的时候断开tail->nex的连接,翻转后再前后连接上即可
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
# python3: 时间 32 ms, 击败 99.84%; 内存 15.7 MB, 击败 99.81% # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]: dummy = ListNode(-1, head) pre = dummy # 进入循环时需建立pre->head的关系,head为下一个待翻转的链表头 while head: # 建立tail->nex的关系,tail为待翻转的链表尾 tail = pre for _ in range(k): tail = tail.next if not tail: return dummy.next nex = tail.next # 把待翻转的链表尾结点和下一个结点断开 tail.next = None # 返回翻转后的新的头指针和尾指针 head, tail = self.reverseList(head) # 把原链表和翻转后的链表给接上 pre.next = head tail.next = nex # 恢复原有的pre和head的关系 pre = tail head = tail.next return dummy.next # 需要断开待翻转链表的尾指针和尾指针的下一个结点的连接 def reverseList(self, head): pre, cur = None, head while cur: curNext = cur.next cur.next = pre pre, cur = cur, curNext # 返回翻转后的新的头指针(pre)和新的尾指针(原来的head) return pre, head// c++: 时间 12 ms, 击败 91.07%; 内存 11.3 MB, 击败 23.80% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) { ListNode dummy = ListNode(-1, head); ListNode *pre = &dummy; while (head != nullptr) { ListNode * tail = head; for (int i = 0; i < k-1; ++i) { tail = tail->next; if (tail == nullptr) { return dummy.next; } } ListNode *nex = tail->next; tail->next = nullptr; tie(head, tail) = reverseList(head); pre->next = head; tail->next = nex; pre = tail; head = nex; } return dummy.next; } pair<ListNode*, ListNode*> reverseList(ListNode * head) { ListNode *pre = nullptr, *cur = head; while (cur != nullptr) { ListNode *curNext = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = curNext; } return {pre, head}; } };// java: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 41.9 MB, 击败 57.91% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head); ListNode pre = dummy; while (head != null) { ListNode tail = pre; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { tail = tail.next; if (tail == null) { return dummy.next; } } ListNode nex = tail.next; tail.next = null; ListNode[] reverse = reverseList(head); head = reverse[0]; tail = reverse[1]; pre.next = head; tail.next = nex; pre = tail; head = nex; } return dummy.next; } private ListNode[] reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null, cur = head; while (cur != null) { ListNode curNext = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = curNext; } return new ListNode[]{pre, head}; } }// go: 时间 8 ms, 击败 14.56%; 内存 3.4 MB, 击败 100% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode { dummy := &ListNode{-1, head} pre := dummy for head != nil { tail := pre for i := 0; i < k; i++ { tail = tail.Next if tail == nil { return dummy.Next } } nex := tail.Next tail.Next = nil head, tail = reverseList(head) pre.Next = head tail.Next = nex pre = tail head = nex } return dummy.Next } func reverseList(head *ListNode) (*ListNode, *ListNode) { var pre *ListNode cur := head for cur != nil { curNext := cur.Next cur.Next = pre pre, cur = cur, curNext } return pre, head }// javascript: 时间 76 ms, 击败 69.37%; 内存 44.1 MB, 击败 73.19% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @param {number} k * @return {ListNode} */ var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) { const dummy = new ListNode(-1, head); let pre = dummy; while (head != null) { let tail = pre; for (let i = 0; i < k; ++i) { tail = tail.next; if (tail == null) { return dummy.next; } } let nex = tail.next; tail.next = null; [head, tail] = reverseList(head); pre.next = head; tail.next = nex; pre = tail; head = nex; } return dummy.next; }; const reverseList = function(head) { let pre = null, cur = head; while (cur != null) { let curNext = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = curNext; } return [pre, head]; }
