160. 相交链表(Intersection of Two Linked Lists)E
英文题目
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
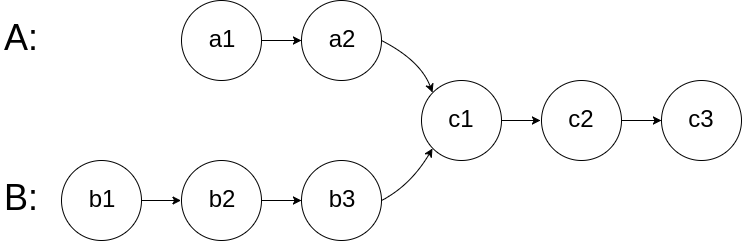
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:

Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.Example 2:
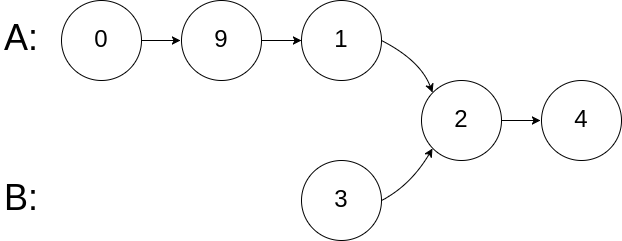
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.Example 3:
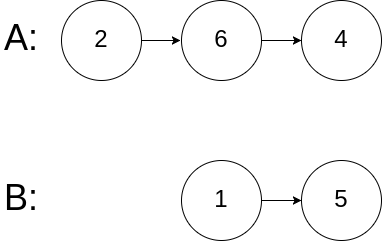
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Each value on each linked list is in the range [1, 10^9].
Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
中文题目
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表**:**

在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:

输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Reference of the node with value = 8 输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。示例 2:

输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Reference of the node with value = 2 输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。示例 3:

输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
哈希集合
用集合存储A链表所有节点,然后遍历B链表查看是否存在
时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(m),m,n 分别是链表headA和headB的长度
# python3: 时间 132 ms, 击败 90.42%; 内存 31.2 MB, 击败 15.61% # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]: visited = set() while headA: visited.add(headA) headA = headA.next while headB: if headB in visited: return headB headB = headB.next return None// c++: 时间 64 ms, 击败 8.48%; 内存 16.8 MB, 击败 12.89% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { unordered_set<ListNode *> visited; while (headA != nullptr) { visited.insert(headA); headA = headA->next; } while (headB != nullptr) { if (visited.find(headB) != visited.end()) { return headB; } headB = headB->next; } return nullptr; } };// java: 时间 5 ms, 击败 20.38%; 内存 45.3 MB, 击败 48% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<>(); while (headA != null) { visited.add(headA); headA = headA.next; } while (headB != null) { if (visited.contains(headB)) { return headB; } headB = headB.next; } return null; } }// go: 时间 32 ms, 击败 34.30%; 内存 7.3 MB, 击败 5.3% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode { visited := map[*ListNode]bool{} for headA != nil { visited[headA] = true headA = headA.Next } for headB != nil { if _, ok := visited[headB]; ok { return headB; } headB = headB.Next } return nil }// javascript: 时间 80 ms, 击败 87.90%; 内存 49 MB, 击败 24% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.next = null; * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} headA * @param {ListNode} headB * @return {ListNode} */ var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) { const visited = new Set(); while (headA != null) { visited.add(headA); headA = headA.next; } while (headB != null) { if (visited.has(headB)) { return headB } headB = headB.next; } return null; };
双指针
思路是:先遍历完自己的链表,再遍历对方的链表
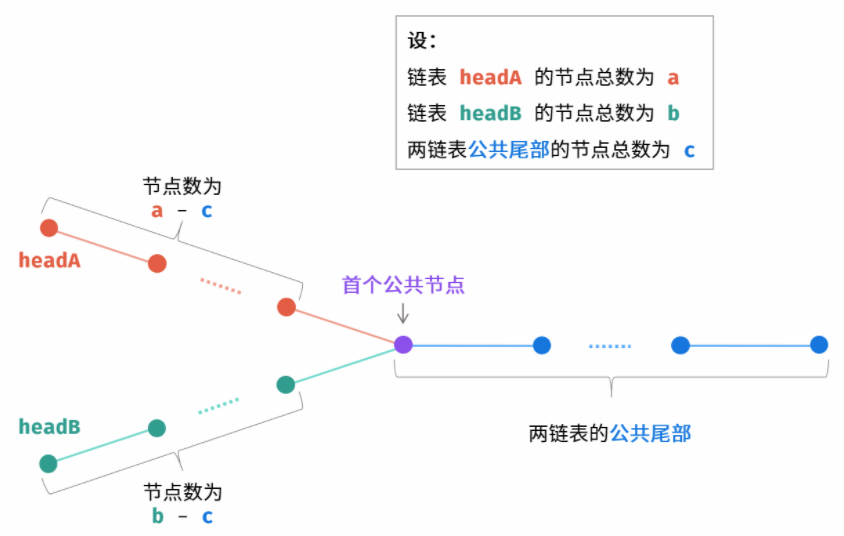
如图,设「第一个公共节点」是node
指针 pA 先遍历完链表 headA ,再开始遍历链表 headB ,当走到 node 时,共走步数为:a + (b - c)
指针 pB 先遍历完链表 headB ,再开始遍历链表 headA ,当走到 node 时,共走步数为:b + (a - c)
此时指针 pA,pB 重合,有两种情况:
1.若两链表有公共尾部(即 c > 0):指针 pA,pB 同时指向「第一个公共节点」node
2.若两链表无公共尾部(即 c = 0):指针 pA,pB 同时指向 null
此时返回 pA 即可(pB也行),它们相等
时间复杂度O(a+b),空间复杂度O(1)
# python3: 时间 144 ms, 击败 54.79%; 内存 31 MB, 击败 25.98% # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode: if not headA or not headB: return None pA, pB = headA, headB # 如果pA,pB当前的节点是存在的,往下走 # 这里还用了个特性,None != None 时,结果是False while pA != pB: pA = pA.next if pA else headB pB = pB.next if pB else headA return pA// c++: 时间 36 ms, 击败 90.22%; 内存 14.3 MB, 击败 40.67% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { if (headA == nullptr || headB == nullptr) { return nullptr; } ListNode *pA = headA, *pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA != nullptr ? pA->next : headB; pB = pB != nullptr ? pB->next : headA; } return pA; } };// java: 时间 1 ms, 击败 98.37%; 内存 45.2 MB, 击败 63.38% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA != null ? pA.next : headB; pB = pB != null ? pB.next : headA; } return pA; } }// go: 时间 28 ms, 击败 74.36%; 内存 6.5 MB, 击败 65.75% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode { if headA == nil || headB == nil { return nil } pA, pB := headA, headB for pA != pB { if pA != nil { pA = pA.Next } else { pA = headB } if pB != nil { pB = pB.Next } else { pB = headA } } return pA }// javascript: 时间 84 ms, 击败 76.76%; 内存 48.1 MB, 击败 89.31% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.next = null; * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} headA * @param {ListNode} headB * @return {ListNode} */ var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } let pA = headA, pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA != null ? pA.next : headB; pB = pB != null ? pB.next : headA; } return pA; };
