145. 二叉树的后序遍历(Binary Tree Postorder Traversal)E
英文题目
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3] 1 \ 2 / 3 Output: [3,2,1]Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]Example 4:
Input: root = [1,2] Output: [2,1]Example 5:
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: [2,1]Constraints:
The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
中文题目
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3] 1 \ 2 / 3 输出: [3,2,1]进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
递归
按照访问左子树-右子树-根节点的顺序遍历
时间复杂度O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次
空间复杂度O(n),为递归过程中栈的开销,平均情况下为 O(log n),最坏情况下树呈现链状,为 O(n)
# python3: 时间 40 ms, 击败 66.43%; 内存 16.2 MB, 击败 6.3% # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def postorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]: self.res = [] self.dfs(root) return self.res def dfs(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None: if not root: return self.dfs(root.left) self.dfs(root.right) self.res.append(root.val)// c++: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 8.2 MB, 击败 37.6% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> res; dfs(res, root); return res; } void dfs(vector<int> &res, TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } dfs(res, root->left); dfs(res, root->right); res.push_back(root->val); } };// java: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 39.8 MB, 击败 35.36% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(res, root); return res; } public void dfs(List<Integer> res, TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } dfs(res, root.left); dfs(res, root.right); res.add(root.val); } }// go: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 1.9 MB, 击败 80.68% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func postorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int { res := []int{} dfs(&res, root) return res } // 特别注意结果数组需要传递引用 func dfs(res *[]int, root *TreeNode) { if root == nil { return } dfs(res, root.Left) dfs(res, root.Right) *res = append(*res, root.Val) }// javascript: 时间 60 ms, 击败 69.29%; 内存 41.1 MB, 击败 46.99% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {number[]} */ var postorderTraversal = function(root) { let res = []; dfs(res, root); return res; }; const dfs = function(res, root) { if (root == null) { return; } dfs(res, root.left); dfs(res, root.right); res.push(root.val); };
迭代
和前序遍历类似,但不同的地方是,这里遍历是先根-右-左的顺序,然后最后逆序
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
# python3: 时间 40 ms, 击败 66.43%; 内存 16.1 MB, 击败 23.49% # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def postorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]: res = [] if not root: return res stack = [root] while stack: node = stack.pop() res.append(node.val) if node.left: stack.append(node.left) if node.right: stack.append(node.right) return res[::-1]// c++: 时间 4 ms, 击败 41.62%; 内存 8 MB, 击败 98.90% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> res; if (root == nullptr) { return res; } stack<TreeNode *> st; st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode * node = st.top(); res.push_back(node->val); st.pop(); if (node->left != nullptr) { st.push(node->left); } if (node->right != nullptr) { st.push(node->right); } } reverse(res.begin(), res.end()); return res; } };// java: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 39.6 MB, 击败 73.40% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return res; } Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.peek(); stack.pop(); res.add(node.val); if (node.left != null) { stack.push(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { stack.push(node.right); } } Collections.reverse(res); return res; } }// go: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 1.9 MB, 击败 100% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func postorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int { res := []int{} if root == nil { return res } stack := []*TreeNode{root} for len(stack) > 0 { node := stack[len(stack)-1] stack = stack[:len(stack)-1] res = append(res, node.Val) if node.Left != nil { stack = append(stack, node.Left) } if node.Right != nil { stack = append(stack, node.Right) } } return reverse(res) } func reverse(nums []int) []int { for i, j := 0, len(nums)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 { nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i] } return nums }// javascript: 时间 60 ms, 击败 69.29%; 内存 41.1 MB, 击败 61.79% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {number[]} */ var postorderTraversal = function(root) { let res = []; if (root == null) { return res; } const stack = [root]; while (stack.length) { node = stack.pop(); res.push(node.val); if (node.left != null) { stack.push(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { stack.push(node.right); } } return res.reverse(); };
Morris遍历
参考:
- https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/solutions/431066/er-cha-shu-de-hou-xu-bian-li-by-leetcode-solution/
- https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/solutions/656142/cer-cha-shu-san-chong-bian-li-qian-zhong-erk2/
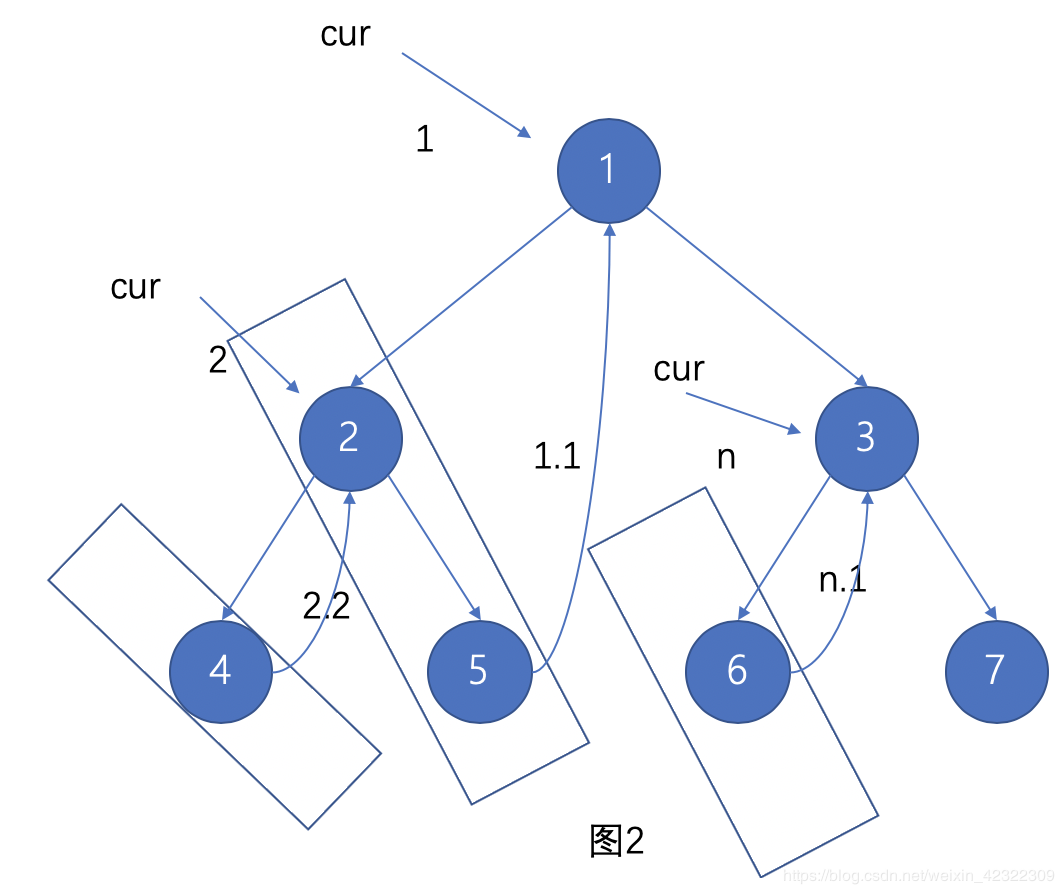
在使用morris遍历的过程中,到达返回根节点,断开子节点到根节点的连接后,对其左子树进行输出,然后将其逆序
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
# python3: 时间 44 ms, 击败 43.37%; 内存 16.2 MB, 击败 6.3% # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def postorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]: res = [] if not root: return res cur = root while cur: curLeft = cur.left if curLeft: while curLeft.right and curLeft.right != cur: curLeft = curLeft.right if not curLeft.right: curLeft.right = cur cur = cur.left continue else: curLeft.right = None self.addPath(res, cur.left) cur = cur.right # 最后一轮循环结束时,从root结点引申的右结点单链表并没有输出,这里补上 self.addPath(res, root) return res def addPath(self, res: List[int], root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None: count = 0 while root: count += 1 res.append(root.val) root = root.right # 翻转 left, right = len(res) - count, len(res) - 1 while left < right: res[left], res[right] = res[right], res[left] left += 1 right -= 1// c++: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 8 MB, 击败 92.68% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> res; if (root == nullptr) { return res; } TreeNode * cur = root; while (cur != nullptr) { TreeNode * curLeft = cur->left; if (curLeft != nullptr) { while (curLeft->right != nullptr && curLeft->right != cur) { curLeft = curLeft->right; } if (curLeft->right == nullptr) { curLeft->right = cur; cur = cur->left; continue; } else { curLeft->right = nullptr; addPath(res, cur->left); } } cur = cur->right; } addPath(res, root); return res; } void addPath(vector<int> &res, TreeNode* root) { int count = 0; while (root != nullptr) { ++count; res.push_back(root->val); root = root->right; } reverse(res.end()-count, res.end()); } };// java: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 39.6 MB, 击败 83.69% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return res; } TreeNode cur = root; while (cur != null) { TreeNode curLeft = cur.left; if (curLeft != null) { while (curLeft.right != null && curLeft.right != cur) { curLeft = curLeft.right; } if (curLeft.right == null) { curLeft.right = cur; cur = cur.left; continue; } else { curLeft.right = null; addPath(res, cur.left); } } cur = cur.right; } addPath(res, root); return res; } private void addPath(List<Integer> res, TreeNode root) { int count = 0; while (root != null) { ++count; res.add(root.val); root = root.right; } int left = res.size() - count, right = res.size() - 1; while (left < right) { int tmp = res.get(left); res.set(left, res.get(right)); res.set(right, tmp); ++left; --right; } } }// go: 时间 0 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 1.9 MB, 击败 100% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func postorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int { res := []int{} if root == nil { return res } cur := root for cur != nil { curLeft := cur.Left if curLeft != nil { for curLeft.Right != nil && curLeft.Right != cur { curLeft = curLeft.Right } if curLeft.Right == nil { curLeft.Right = cur cur = cur.Left continue } else { curLeft.Right = nil addPath(&res, cur.Left) } } cur = cur.Right } addPath(&res, root) return res } func addPath(res *[]int, root *TreeNode) { resSize := len(*res) for root != nil { *res = append(*res, root.Val) root = root.Right } // 此处用了切片的特性,对切片数据更改是共享的 reverse((*res)[resSize:]) } func reverse(nums []int) []int { for i, j := 0, len(nums)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 { nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i] } return nums }// javascript: 时间 60 ms, 击败 69.29%; 内存 41.2 MB, 击败 30.44% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {number[]} */ var postorderTraversal = function(root) { let res = []; if (root == null) { return res; } let cur = root; while (cur != null) { let curLeft = cur.left; if (curLeft != null) { while (curLeft.right != null && curLeft.right != cur) { curLeft = curLeft.right; } if (curLeft.right == null) { curLeft.right = cur; cur = cur.left; continue; } else { curLeft.right = null; addPath(res, cur.left); } } cur = cur.right; } addPath(res, root); return res; }; const addPath = function(res, root) { let count = 0; while (root != null) { ++count; res.push(root.val); root = root.right; } let left = res.length - count, right = res.length - 1; while (left < right) { [res[left], res[right]] = [res[right], res[left]]; ++left; --right; } }
