236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先(Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree)M
英文题目
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:
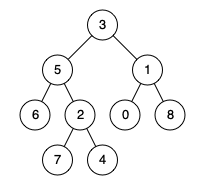
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 Output: 3 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 Output: 5 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 Output: 1Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 10^5].
-10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9
All Node.val are unique.
p != q
p and q will exist in the tree.
中文题目
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出:3 解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。示例 2:
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 输出:5 解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 输出:1提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [2, 10^5] 内。
-10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9
所有 Node.val 互不相同 。
p != q
p 和 q 均存在于给定的二叉树中。
递归
想清楚递归函数的返回值代表的意义:如果不为空,则包含p或q的子节点,或都包含,然后根据左右子节点是否为空,判断公共祖先,并逐级往上传
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
# python3: 时间 68 ms, 击败 76.86%; 内存 28.3 MB, 击败 13.73% # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution: def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode': # 终止条件: # 1.当越过叶子节点,直接返回None # 2.当root等于p、q,直接返回root if not root or root == p or root == q: return root # 递归左右子节点 left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q) right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q) # 返回值有4种情况: # 1.当 left 和 right 同时为空:说明 root 的左/右子树中 # 都不含p,q,返回None if not left and not right: return None # 3.当 left 为空,right 不为空:p,q 都不在 root 的左子树中, # 直接返回 right,有两种情况 # 1. p,q 其中一个在 root 的右子树中,此时 right 指向其中一个节点 # 2. p,q 两节点都在 root 的右子树中,此时 right 指向最近公共祖先节点 elif not left: return right elif not right: return left # 2.如果 left 和 right 同时不为空,说明 p,q 分别在 root # 的左右子树,root 为最近公共祖先,返回root return root// c++: 时间 68 ms, 击败 76.86%; 内存 28.3 MB, 击败 13.73% # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution: def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode': if not root or root == p or root == q: return root left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q) right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q) if not left and not right: return None if not left: return right if not right: return left return root// java: 时间 6 ms, 击败 99.83%; 内存 42.4 MB, 击败 67.80% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { return root; } TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if (left == null && right == null) { return null; } else if (left == null) { return right; } else if (right == null) { return left; } return root; } }// go: 时间 4 ms, 击败 99.38%; 内存 6.8 MB, 击败 95.99% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode { if root == nil || root == p || root == q { return root } left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q) right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q) if left == nil && right == nil { return nil } else if left == nil { return right } else if right == nil { return left } return root }// javascript: 时间 76 ms, 击败 65.78%; 内存 50.4 MB, 击败 44.51% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.left = this.right = null; * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @param {TreeNode} p * @param {TreeNode} q * @return {TreeNode} */ var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) { if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { return root; } let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if (left == null && right == null) { return null; } else if (left == null) { return right; } else if (right == null) { return left; } return root; };
存储父节点
注意,该解法能成立的条件是,所有节点的val均不相同
遍历存储所有节点为哈希表,key是节点值,value是父节点
从p节点不断向上遍历,并记录其访问过的节点,直到根节点,再从q节点不断向上遍历直至已访问过的节点
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
# python3: 时间 72 ms, 击败 60.26%; 内存 28.3 MB, 击败 11.33% # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution: def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode': self.father = {root.val: None} self.dfs(root) self.visited = set() while p != None: self.visited.add(p.val) p = self.father[p.val] while q != None: if q.val in self.visited: return q q = self.father[q.val] return None def dfs(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None: if root.left: self.father[root.left.val] = root self.dfs(root.left) if root.right: self.father[root.right.val] = root self.dfs(root.right)// c++: 时间 20 ms, 击败 34.71%; 内存 17.2 MB, 击败 4.99% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { unordered_map<int, TreeNode*> father; father[root->val] = nullptr; dfs(father, root); unordered_set<int> visited; while (p != nullptr) { visited.insert(p->val); p = father[p->val]; } while (q != nullptr) { if (visited.find(q->val) != visited.end()) { return q; } q = father[q->val]; } return nullptr; } void dfs(unordered_map<int, TreeNode*> & father, TreeNode* root) { if (root->left != nullptr) { father[root->left->val] = root; dfs(father, root->left); } if (root->right != nullptr) { father[root->right->val] = root; dfs(father, root->right); } } };// java: 时间 9 ms, 击败 15.52%; 内存 43.8 MB, 击败 5.40% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { Map<Integer, TreeNode> father = new HashMap<>(); father.put(root.val, null); dfs(father, root); Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>(); while (p != null) { visited.add(p.val); p = father.get(p.val); } while (q != null) { if (visited.contains(q.val)) { return q; } q = father.get(q.val); } return null; } private void dfs(Map<Integer, TreeNode> father, TreeNode root) { if (root.left != null) { father.put(root.left.val, root); dfs(father, root.left); } if (root.right != null) { father.put(root.right.val, root); dfs(father, root.right); } } }// go: 时间 12 ms, 击败 49.15%; 内存 7.6 MB, 击败 8.58% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode { father := map[int]*TreeNode{root.Val: nil} dfs(father, root) visited := map[int]bool{} for p != nil { visited[p.Val] = true p = father[p.Val] } for q != nil { if _, ok := visited[q.Val]; ok { return q } q = father[q.Val] } return nil } func dfs(father map[int]*TreeNode, root *TreeNode) { if root.Left != nil { father[root.Left.Val] = root dfs(father, root.Left) } if root.Right != nil { father[root.Right.Val] = root dfs(father, root.Right) } }// javascript: 时间 76 ms, 击败 65.78%; 内存 51.9 MB, 击败 5.1% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.left = this.right = null; * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @param {TreeNode} p * @param {TreeNode} q * @return {TreeNode} */ var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) { const father = new Map([[root.val, null]]); dfs(father, root); const visited = new Set(); while (p != null) { visited.add(p.val); p = father.get(p.val); } while (q != null) { if (visited.has(q.val)) { return q; } q = father.get(q.val); } return null; }; const dfs = function(father, root) { if (root.left != null) { father.set(root.left.val, root); dfs(father, root.left); } if (root.right != null) { father.set(root.right.val, root); dfs(father, root.right); } }
