1143. 最长公共子序列(Longest Common Subsequence)M
英文题目
Given two strings text1 and text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence. If there is no common subsequence, return 0.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
For example, "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde".
A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
Example 1:
Input: text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" Output: 3 Explanation: The longest common subsequence is "ace" and its length is 3.Example 2:
Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc" Output: 3 Explanation: The longest common subsequence is "abc" and its length is 3.Example 3:
Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "def" Output: 0 Explanation: There is no such common subsequence, so the result is 0.Constraints:
1 <= text1.length, text2.length <= 1000
text1 and text2 consist of only lowercase English characters.
中文题目
给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长公共子序列的长度。
一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
例如,"ace" 是 "abcde" 的子序列,但 "aec" 不是 "abcde" 的子序列。两个字符串的「公共子序列」是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
若这两个字符串没有公共子序列,则返回 0。
示例 1:
输入:text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" 输出:3 解释:最长公共子序列是 "ace",它的长度为 3。示例 2:
输入:text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc" 输出:3 解释:最长公共子序列是 "abc",它的长度为 3。示例 3:
输入:text1 = "abc", text2 = "def" 输出:0 解释:两个字符串没有公共子序列,返回 0。提示:
1 <= text1.length <= 1000
1 <= text2.length <= 1000
输入的字符串只含有小写英文字符。
动态规划
dp[i][j]表示字符串 A 的 i 号位和 B 的 j 号位之前的LCS长度(下标从0开始)
有两种情况:
1.若A[i]==B[j],则字符串A与字符串B的LCS增加了1位,既有dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j]+1
2.若A[i]!=B[j],则字符串A的i号位无法延长,因此dp[i+1][j+1]将会继承dp[i][j+1]与dp[i+1][j]中的较大值
状态转移方程:
边界:
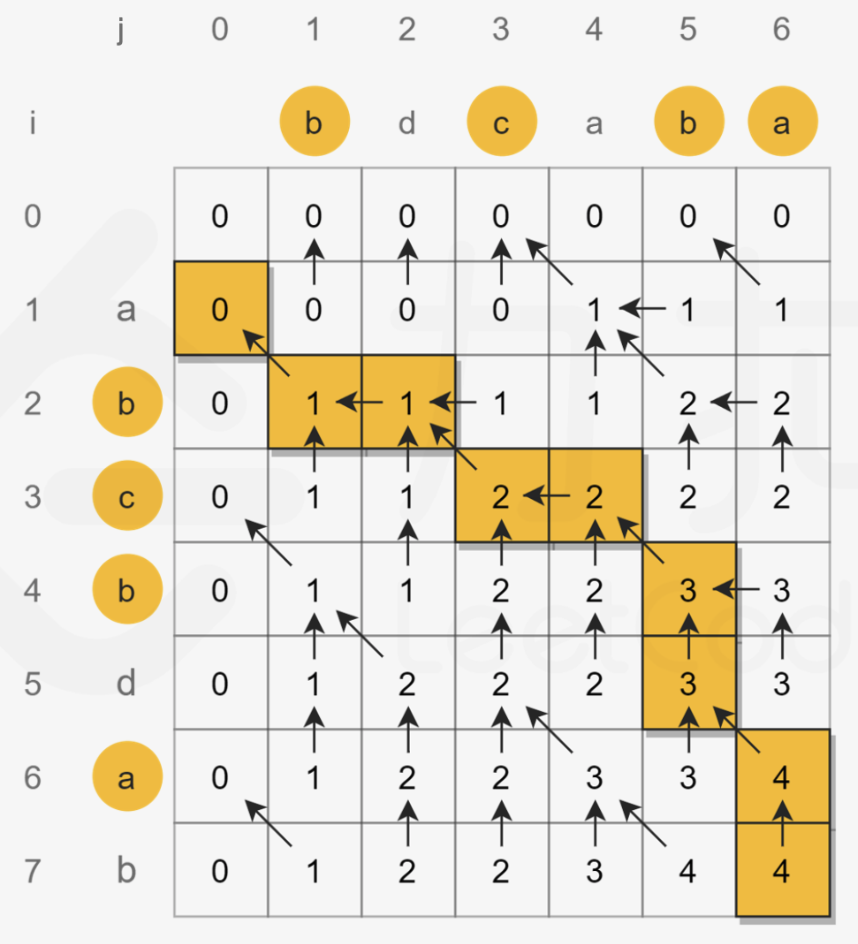
时间复杂度:O(mn),空间复杂度:O(mn)
# python3: 时间 652 ms, 击败 92.38%; 内存 40.9 MB, 击败 41.15% class Solution: def longestCommonSubsequence(self, text1: str, text2: str) -> int: l1, l2 = len(text1), len(text2) dp = [[0] * (l2+1) for _ in range(l1+1)] for i in range(l1): for j in range(l2): if text1[i] == text2[j]: dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j] + 1 else: dp[i+1][j+1] = max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]) return dp[l1][l2]// c++: 时间 52 ms, 击败 69.53%; 内存 24 MB, 击败 9.45% class Solution { public: int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int l1 = text1.size(), l2 = text2.size(); vector<vector<int>> dp((l1+1), vector<int>((l2+1), 0)); for (int i = 0; i < l1; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < l2; ++j) { if (text1[i] == text2[j]) { dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j] + 1; } else { dp[i+1][j+1] = max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]); } } } return dp[l1][l2]; } };// java: 时间 18 ms, 击败 69.39%; 内存 47.3 MB, 击败 70.11% class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { int l1 = text1.length(), l2 = text2.length(); int[][] dp = new int[l1+1][l2+1]; for (int i = 0; i < l1; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < l2; ++j) { if (text1.charAt(i) == text2.charAt(j)) { dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j] + 1; } else { dp[i+1][j+1] = Math.max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]); } } } return dp[l1][l2]; } }// go: func longestCommonSubsequence(text1 string, text2 string) int { l1, l2 := len(text1), len(text2) dp := make([][]int, l1+1) for i := 0; i < l1+1; i++ { dp[i] = make([]int, l2+1) } for i := 0; i < l1; i++ { for j := 0; j < l2; j++ { if text1[i] == text2[j] { dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j] + 1 } else { dp[i+1][j+1] = maxInt(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]) } } } return dp[l1][l2]; } func maxInt(i, j int) int { if i > j { return i } return j }// javascript: 时间 128 ms, 击败 33.27%; 内存 67.7 MB, 击败 59.8% /** * @param {string} text1 * @param {string} text2 * @return {number} */ var longestCommonSubsequence = function(text1, text2) { const l1 = text1.length, l2 = text2.length; const dp = new Array(l1+1).fill(0).map(() => new Array(l2+1).fill(0)); for (let i = 0; i < l1; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < l2; ++j) { if (text1.charAt(i) == text2.charAt(j)) { dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j] + 1; } else { dp[i+1][j+1] = Math.max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]); } } } return dp[l1][l2]; };
