2.两数相加(Add Two Numbers)M
英文题目
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
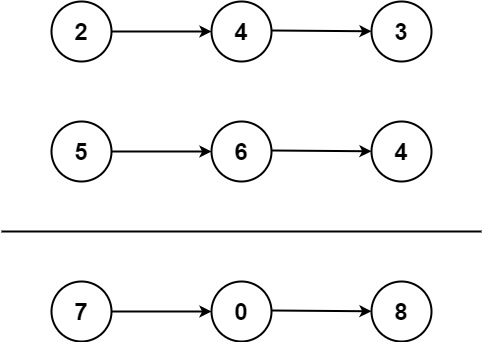
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]Constraints:
The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range [1, 100].
0 <= Node.val <= 9
It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
中文题目
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:

输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,0,8] 解释:342 + 465 = 807.示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] 输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]提示:
每个链表中的节点数在范围 [1, 100] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 9
题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
模拟
类似字符串相加的方法
时间复杂度 O(max(m,n)),空间复杂度O(1)
# python: 时间 60 ms, 击败 68.77%; 内存 16 MB, 击败 51.65% # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next from typing import Optional class Solution: def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: dummy = ListNode(-1) cur = dummy carry = 0 while l1 or l2: n1, n2 = 0, 0 if l1: n1 = l1.val l1 = l1.next if l2: n2 = l2.val l2 = l2.next tmp = n1 + n2 + carry carry = tmp // 10 cur.next = ListNode(tmp % 10) cur = cur.next if carry > 0: cur.next = ListNode(carry) return dummy.next// c++: 时间 20 ms, 击败 91.91%; 内存 69.6 MB, 击败 89.18% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode* cur = dummy; int carry = 0; while (l1 != nullptr || l2 != nullptr) { int n1 = 0, n2 = 0; if (l1 != nullptr) { n1 = l1->val; l1 = l1->next; } if (l2 != nullptr) { n2 = l2->val; l2 = l2->next; } int tmp = n1 + n2 + carry; cur->next = new ListNode(tmp % 10); carry = tmp / 10; cur = cur->next; } if (carry > 0) { cur->next = new ListNode(carry); } return dummy->next; } };// java: 时间 1 ms, 击败 100%; 内存 41.9 MB, 击败 48.53% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode cur = dummy; int carry = 0; while (l1 != null || l2 != null) { int n1 = 0, n2 = 0; if (l1 != null) { n1 = l1.val; l1 = l1.next; } if (l2 != null) { n2 = l2.val; l2 = l2.next; } int tmp = n1 + n2 + carry; cur.next = new ListNode(tmp % 10); cur = cur.next; carry = tmp / 10; } if (carry > 0) { cur.next = new ListNode(carry); } return dummy.next; } }// go: 时间 16 ms, 击败 12.86%; 内存 4.3 MB, 击败 89.43%p /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode { dummy := &ListNode{Val: -1} cur := dummy carry := 0 for l1 != nil || l2 != nil { n1, n2 := 0, 0 if l1 != nil { n1 = l1.Val l1 = l1.Next } if l2 != nil { n2 = l2.Val l2 = l2.Next } tmp := n1 + n2 + carry cur.Next = &ListNode{Val: tmp % 10} cur = cur.Next carry = tmp / 10 } if carry > 0 { cur.Next = &ListNode{Val: carry} } return dummy.Next }// javascript: 时间 104 ms, 击败 46.23%; 内存 45.9 MB, 击败 61.39% /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} l1 * @param {ListNode} l2 * @return {ListNode} */ var addTwoNumbers = function(l1, l2) { let dummy = new ListNode(-1); let cur = dummy; let carry = 0; while (l1 || l2) { // 注意判空的方法 let n1 = 0, n2 = 0; if (l1) { n1 = l1.val; l1 = l1.next; } if (l2) { n2 = l2.val; l2 = l2.next; } let tmp = n1 + n2 + carry; cur.next = new ListNode(tmp % 10); cur = cur.next; carry = Math.floor(tmp / 10); // 注意算截断的方法 } if (carry > 0) { cur.next = new ListNode(carry); } return dummy.next; };
